Enable NAT
Enable DHCP Server
DNS Proxy and Port Forwarding settings
(i.e. if the MAC is 00:15:6D:A3:04:FB, Generated unique Auto IP will be 169.254.4.251).
IP Aliases: for internal and external network interface can be configured. IP Aliases can be specified using the IP Aliases configuration
window that is opened while activating the "Configure" button.
IP Address is the alternative IP address for the LAN or WLAN interface, which can be used for the routing or device management
purposes;
Netmask is the network address space identifier for the particular IP Alias;
Comments is the informal field for the comment of the particular IP Alias. Few words about the alias purpose are saved there usually;
Enabled flag enables or disables the particular IP Alias. All the added IP Aliases are saved in the system configuration file. However,
only the enabled IP Aliases will be active during the AirOS system operation.
Change MAC Address: When checked, the MAC address of the respective interface may be changed easily. This is especially useful if
your ISP only assigns one valid IP address associated to a specific MAC address; usually used by Cable operators or some WISP.
LAN Network Settings
IP Address: This is the IP addresses to be represented by the LAN (including WLAN) interface that is connected to the internal network.
This IP will be used for the routing of the internal network (it will be the Gateway IP for all the devices connected on the internal
network). This is the IP address can be used for the management purpose of the AirOS v5.3 powered device.
Netmask: This is used to define the device IP classification for the chosen IP address range. 255.255.255.0 is a typical netmask value for
Class C networks, which support IP address range 192.0.0.x to 223.255.255.x. Class C network Netmask uses 24 bits to identify the
network (alternative notation "/24") and 8 bits to identity the host.
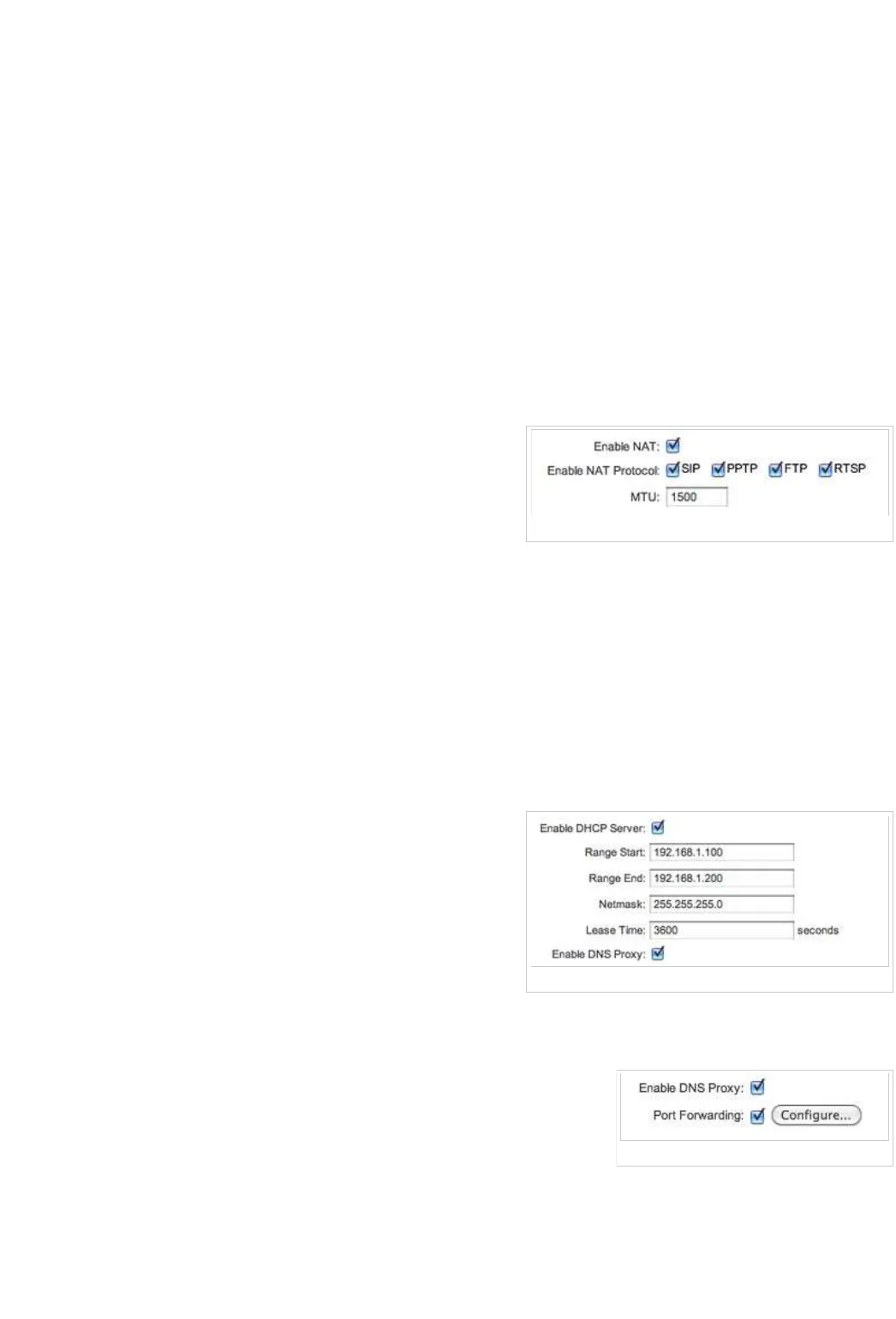
Enable NAT: Network Address Translation (NAT) enables packets to be sent
from the external network (WAN) to the local interface IP address and then
sub-routed to other client devices residing on it's local network while the AirOS
powered device is operating in AP/AP WDS wireless mode.
Enable NAT Protocol: While NAT is enabled, data packets could be
modified in order to allow pass-through to the Router. To avoid packets
modification of some specific packets, like: SIP, PPTP, FTP, RTSP; uncheck the respective checkbox (-es).
NAT is implemented using the masquerade type firewall rules. NAT firewall entries are stored in the iptables nat table, while the device
is operating in Router mode. Please refer to the iptables tutorial (http://iptables-tutorial.frozentux.net/iptables-
tutorial.html#MASQUERADETARGET) for detailed description of the NAT functionality in Router mode.
Static routes should be specified in order the packets should pass-through the AirOS v5.3 based device if the NAT is disabled in while
operating in SOHO Router network mode.
MTU: defines the size (in bytes) of the largest protocol data unit the layer can pass on. When using slow links, large packets can cause
some delays thereby increasing lag and latency.
Enable DHCP Server: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server assigns IP addresses to clients that will associate to the
wireless interface while the AirOS powered device is operating in AP/AP WDS wireless mode and assigns IP addresses to clients, which
will connect to the LAN interface while the AirOS powered device is operating in Station/Station WDS mode.
Range Start/End: This range determines the IP addresses given out by the
DHCP server to client devices on the internal network that use dynamic IP
configuration.
Netmask: This is used to define the device IP classification for the chosen IP
address range. 255.255.255.0 is a typical netmask value for Class C
networks, which support IP address range 192.0.0.x to 223.255.255.x. Class
C network Netmask uses 24 bits to identify the network (alternative notation
"/24") and 8 bits to identity the host.
Lease Time: The IP addresses given out by the DHCP server will only be
valid for the duration specified by the lease time. Increasing the time ensure
client operation without interrupt, but could introduce potential conflicts. Lowering the lease time will avoid potential address
conflicts, but might cause more slight interruptions to the client while it will acquire new IP addresses from the DHCP server. The
time is expressed in seconds.
Enable DNS Proxy: The DNS Proxy forwards the Domain Name System requests from the
hosts that reside in the internal network to the DNS server while AirOS powered device is in
operating in SOHO Router mode. Valid Primary DNS Server IP needs to be specified for DNS
Proxy functionality. Internal network interface IP of the AirOS powered device should be
specified as the DNS server in the host configuration in order DNS Proxy should be able to get
the DNS requests and translate domain names to IP addresses afterwards.
Port Forwarding: Port forwarding allows specific ports of the hosts residing in the internal network to be forwarded to the external
network (WAN). This is useful for number of applications such as FTP servers, voip, gaming, etc. where different host systems need to be
seen using a single common IP address/port.
Port Forwarding rules can be set in Port Forwarding window, which is opened by enabling the Port Forwarding option and activating the
Configure button.
AirOS 5.3 - Ubiquiti Wiki
http://www.ubnt.com/wiki/AirOS_5.3
22 van 34 14-4-2011 21:46










