Section 2 System Overview
Section 2 System Overview
The Olympus Fluoview is a confocal scanning type laser fluorescent microscope that utilizes a common
focal point optical system to realize high resolution and high contrast as well as a spectacular
improvement in resolution in the optical axis.
This microscope provides researchers with the ability to perform automatic sectioning, three-dimensional
structuring and time fluctuation observation as well as various types of image processing and analysis.
2-1 Principle of Operation
Light detector
The scanning laser microscope focuses the laser beam into a tiny spot through the objective lens
and scans specimens in the X and Y directions.
The scan unit detects fluorescent and transmitted light from specimens and outputs specimen
images to the image monitor.
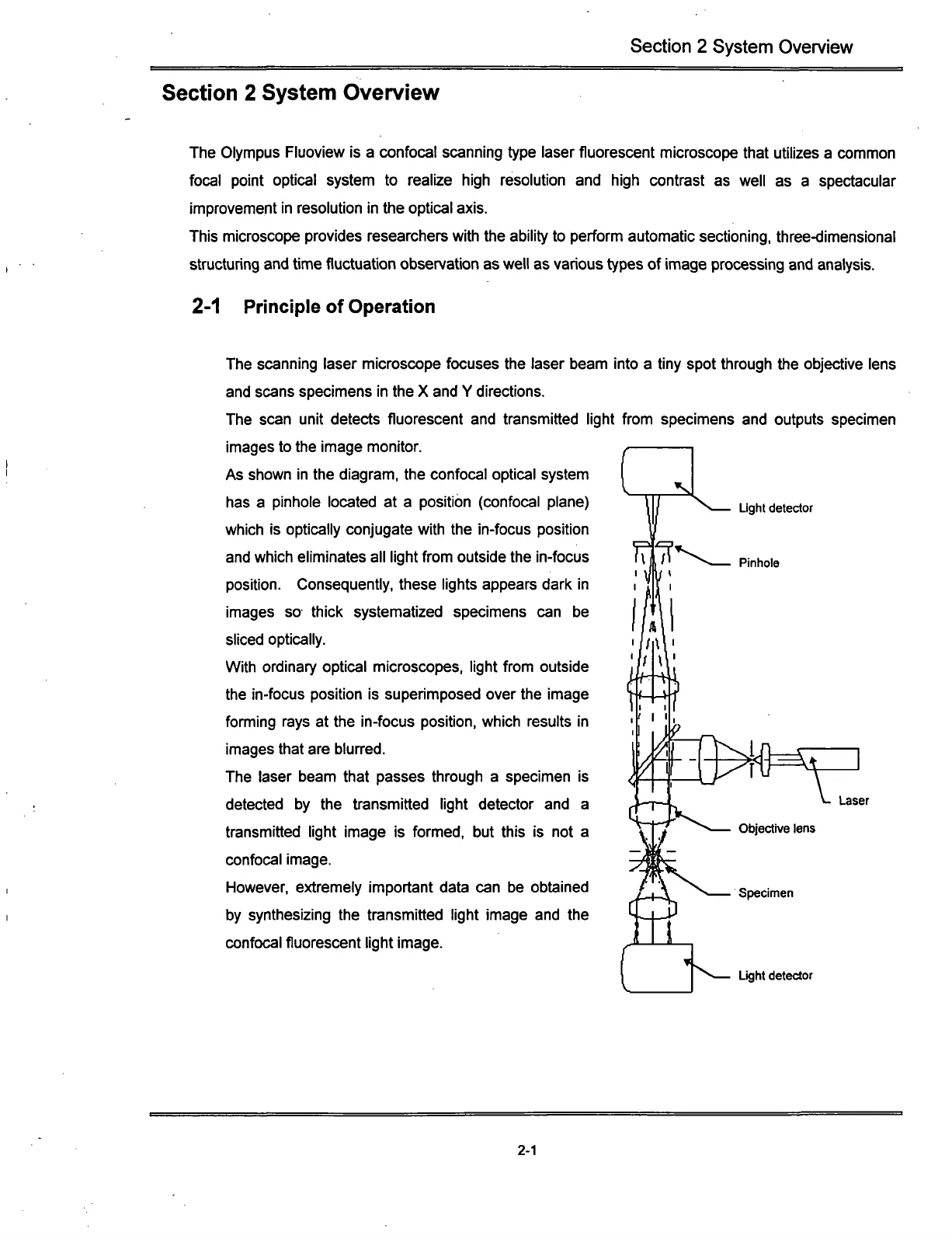
As shown in the diagram, the confocal optical system
has a pinhole located at a position (confocal plane)
which is optically conjugate with the in-focus position
and which eliminates all light from outside the in-focus
position.
Consequently, these lights appears dark in
images so thick systematized specimens can be
sliced optically.
With ordinary optical microscopes, light from outside
the in-focus position is superimposed over the image
fomiing rays at the in-focus position, which results in
images that are blurred.
The laser beam that passes through a specimen is
detected by the transmitted light detector and a
transmitted light image is formed, but this is not a
confocal image.
However, extremely important data can be obtained
by synthesizing the transmitted light image and the
confocal fluorescent light image.
Light detector
c)^
Laser
Objective lens
Specimen
2-1










