Advantech SOM-Express Design Guide
90 Chapter 5 Carrier Board Design Guidelines
5.12.4.5 ESD Protection
The PCB must incorporate protection against electrostatic discharge (ESD) events
that might enter at I/O signal and electrical connection points. The goal is to prevent
component or system failures due to externally sourced ESD impulses that may be
propagated through both radiated and conducted mechanisms.
Several commonly used design techniques for ESD protection that may be
implemented on a PC for high-level pulse suppression include the following:
1. High voltage capacitors. These disc-ceramic capacitors must be rated at
1500 V (1 KV) minimum. Lower-voltage capacitors may be damaged by the
first occurrence of an ESD pulse. This capacitor must be located
immediately adjacent to the I/O connector.
2. TVS components. These are semiconductor devices specifically designed
for transient voltage suppression applications. They have the advantage of
a stable and fast time constant to avalanche, and a stable clamping level
after avalanche.
3. LC filters. An LC filter is a combination of an inductor and a capacitor to
ground. This constitutes a low-pass LC filter that prevents high-frequency
ESD energy from entering the system. The inductor presents a high-
impedance source to the pulse, thus attenuating the impulse energy that
enters the system. The capacitor, located on the input side of the inductor
will shunt high-frequency ESD spectral level components to ground. An
additional benefit of this circuit combination is enhancement of radiated EMI
noise suppression.
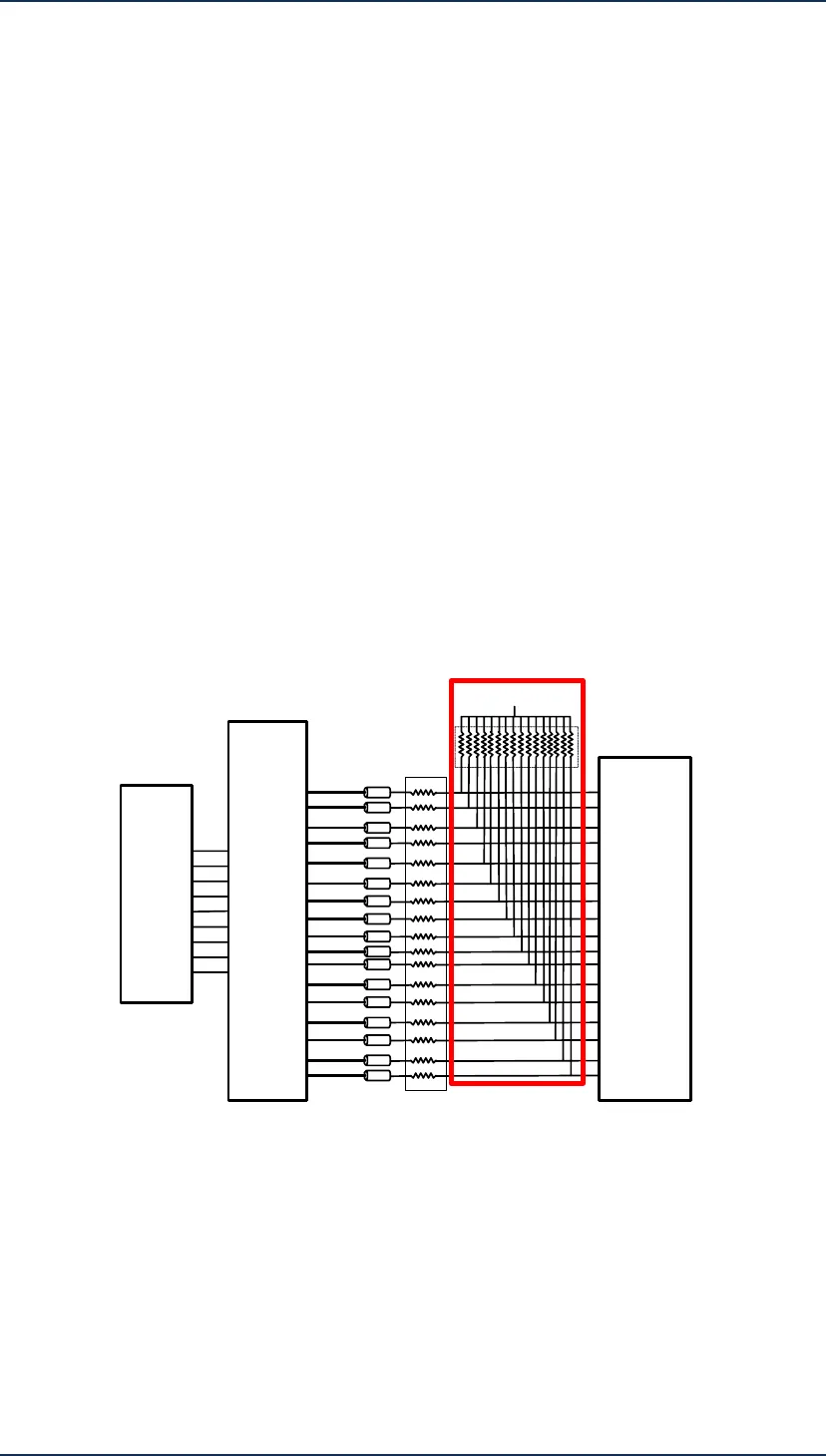
33 ohm
4.7k ohm
VCC
Super I/O
Parallel Port
D-Sub 25
Route to Minimum
Strobe#
Data 0
Acknowledge
Select Input
Select
Out of Paper
Busy
Data 1
Data 2
Data 3
Data 4
Data 5
Data 6
Data 7
AutoFeed#
Error#
Initial
SOM-
Express
LPC_AD[0]
LPC_AD[1]
LPC_AD[2]
LPC_AD[3]
LPC_FRAME#
LPC_DRQ[0]
LPC_DRQ[1]
LPC_SERIRQ
LPC_CLK
Figure 5-57 LPT Connection










